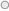Due to complexity involved in raising funds from various sources available in the market, micro, small and medium enterprises are unable to get the needed financial support on time at reasonable cost easily. In order to assist these unfunded entrepreneurs and small business concerns, the present Government led by Shri Narendra Modi, started MUDRA bank on 8thApril, 2015 with a corpus of ₹20,000 crore and a credit guarantee fund of ₹3,000 crore to support financial institutions and micro finance institutions. MUDRA bank was formed with a mandate to refinance and regulate micro finance institutions and give financial assistance to micro and small units that are typically excluded from the mainstream banking system. The scheme was launched as a refinancing institution to provide funding support to the lending institutions engaged in financing micro units in the country, through the Government of India’s flagship programme. MUDRA scheme is not only to bridge the funding gap to the micro enterprises but also aims to boost the confidence of the first generation entrepreneurs and also assist existing small businesses expand their business activities in more diversified ways. As on 31st March 2018, the MUDRA scheme has provided financial support to 4, 81,30,593 entrepreneurs with a total amount of ₹246437.40 crore in promotion of new and existing enterprises in the country.
MSME sector is the second largest employment provider in our country and it is good vehicle to achieve inclusive and distributed growth. As per the report of NSS 73rd round there are 18.91 lakhs of MSMEs with a total employment capacity of 29.18 lakhs spreading in the entire eight sister states of Northeast India as on 31st December 2017. Most of these MSMEs are facing number of problems of sustaining its operation smoothly such as Access to Finance, Lack of growth orientation, Skill Development Gaps, Policy Advocacy Needs, Lack of Market Development/ Market Making, Knowledge Gaps, Information Asymmetry and Entry Level Technologies. The biggest bottleneck to the growth of entrepreneurship is lack of financial support to this sector. The support from the Banks to this sector is meagre, with less than 15% of bank credit going to Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs). The MUDRA loans provided for the last four years has shown a great relieve of these MSMEs not only in the region but also in the whole states of the country.
MUDRA will refinance all banks, Micro-finance Institutions (MFIs) and other lending institutions, which are in the business of lending to micro/ small business entities, engaged in manufacturing, trading and services activities. The MUDRA loans are provided for income generating small business activity in manufacturing, processing, and service sector and trading concern. The Project cost is decided based on business plan and the investment proposed.
Before switch over to the performance appraisal of MUDRA bank finance in the region, it is very much essential to know the status and position of Microfinance and commercial banks in the region. These financial institutions are the key role in refinancing the financial assistance to micro, small and medium enterprises in the region whose financial requirement is below ₹10 lakh.
Status of Microfinance in Northeast India
National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) takes pride in the fact that the Self Help Group - Bank Linkage Programme, which is the largest microfinance programme in the world, today touches nearly 11 crore households through more than 87 lakh SHGs with deposits of over ₹19,500 crore and annual loan off take of more than ₹47,000 crore and loans outstanding over ₹75,500 crore, it is probably the world’s most widely participated grassroots oriented microfinance programme as on 31st March 2018.
Banking Profile of Northeast India
After 70 years of Independence, Northeast India is industrially and economically backward region of the country. Still almost all the states of the region’s economy are depending on agriculture. Contribution from the secondary and tertiary sectors to the economy is very negligible.
Below given data shows the banking profile and average population per bank office in the region. Among the sister states of the region, Sikkim emerged as the least number of populations per bank office. Lesser the number of populations provide the better banking facilities to the customer. On the other hand Manipur place the largest number of populations covered by a bank office as on census 2011. Further it is also found that the states of Assam, Manipur and Nagaland have exceeded their average population per bank than the average population per bank of Northeast India. Other states are below the average of Northeast India.
MUDRA finance in Northeast India
As we have seen from the previous table regarding the average population per bank office in the region. Average population per bank office in the region is 9804 as on 2011 census and 10891 (projected) as on 2018. This data has clearly shown the poor coverage of population per banks as a result most of the clients are not getting the proper banking facilities from the bank and financial institutions operating in the region. It is also true that one of the most important factors for backwardness of industry is lack of proper source of finance. As the region provide less banking facilities towards the unfunded entrepreneurs, their prospect of growth declines.
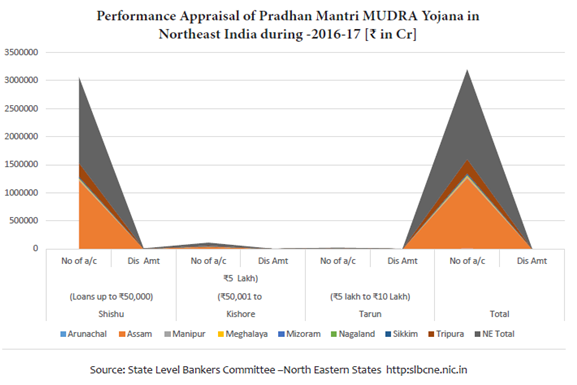
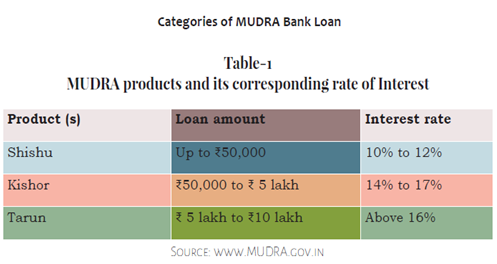
At this fag end introduction of Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana in 2015 has given a new dimension for growth of MSME in the region. Following shows the number of enterprises, amount sanctioned and disbursed under MUDRA finance scheme in the entire eight sister 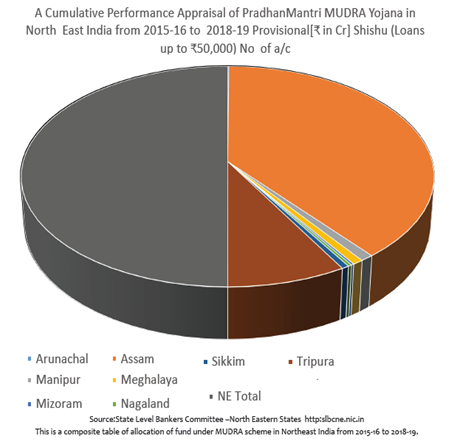 states of Northeast India during 2015-16. It is also seen that the fund has been allocated to Shishu, Kishore and Tarun categories of enterprises. Among the sister states, Assam state occupied the big sister’s role which cannot be comparable with other states of the region. Keeping aside the Assam state, among the seven small states of the region, Tripura state occupied the prominent place in all the three categories of scheme followed by Manipur state in Shishu category and Meghalaya state in both Kishore and Tarun categories respectively.
states of Northeast India during 2015-16. It is also seen that the fund has been allocated to Shishu, Kishore and Tarun categories of enterprises. Among the sister states, Assam state occupied the big sister’s role which cannot be comparable with other states of the region. Keeping aside the Assam state, among the seven small states of the region, Tripura state occupied the prominent place in all the three categories of scheme followed by Manipur state in Shishu category and Meghalaya state in both Kishore and Tarun categories respectively.
To read the further article please get your copy of Eastern Panorama March issue @http://www.magzter.com/IN/Hill-Publications/Eastern-Panorama/News/ or mail to contact @easternpanorama.in