Downfall of The Rupee
Fall,fall and fall,is the story of Indian rupee.At the time of writing this article,the price of one dollar was 65,the lowest ever in the history of India.
The increase in the cost of the dollar means increase inflation in the country,which gives rise to increase in the cost of living.The foreign tours and foreign studies will be more expensive and import too will be expensive. It will weigh heavily on our economy.
The main reason for the fall of rupee is that the US Federation Reserve has hinted at winding down the program to pump in billions of dollars in view of improved recovery in economy.Part of this money comes to India as Indian equities.Portfolio investors are now withdrawing money from the dollar and pulling down the local currency,the rupee.
CURRENCY DEFICIATION
If the currency is deficiating it implies that its value has fallen in relation to another currency.In the present context,the value of rupee has fallen or deficiated from about Rs.55 to about Rs.65 in three months.It directly affects people/institutions like banks,brokers,government trading currencies etc.This explains why the currency price fluctuation is seen every day.
EXCHANGE RATE
Exchange rate–what is it all about?Like any other commodity,the exchange rate of a price of a currency is determined by laws of demand and supply.Stronger demand for the currency pushes up its price and vice versa.An exchange rate of Rs.65 to a dollar simply means that the value of $ 1 US is equivalent to Rs.65.
|
1947 Rs 1=$ 1 1966 Rs 6.35=$1 Govt.devalues rupee to encourage export 1973 Rs 7.67=$1 Oil crisis breaks out:govt.enacts FERA to clamp down on illegal forex transactions. 1975 Rs 8.41=$1 Political emergency 1985 Rs 12.36=$1
1991 Rs 22.69=$1 India escapes payment crisis by mortgaging gold.Manmohan Singh dissembles industrial license regime and begins economic reforms in India.
Security Exchange Board to India set up to regulate stock market. 2002 Rs 48.60=$1 Money laundering act enacted preventing illegal monetary transaction across countries. 1998 Rs 41.27=$1 2004 Rs 45.32=$1 UPA govt with Manmohan Singh as PM comes to power. 2008 Rs 43.50=$1 Lehman Brother collapses. 1993 Rs 31.44=$1 India merges dual rates of liberalized exchange rate management system. 1996 Rs 35.43=$1 Import licensing abolished and tariffs brought down substantially. 1997 Rs 36.32=$1 2010 Rupee gets a new symbol 2006 Rs 45.31=$1 India’s growth rate hits a record 9.8% on the back of high domestic and global demand. 2009 Rs 48.40=$1 UPA govt.returns to power 1947 Anna (1/16 of Rs 1) For 1 Anna you could get mix chaat which today would cost you Rs.30 UNTIL 1957 Government fixed price rate for atta was 6 1/2 anna for 1 seer(1seer = 80 tolas 1kg = 86 tolas)and after the introduction of decimal system it was 44 paise per kilogram. 1970 83 PAISA In the 1970s,a litre of petrol cost 83 paise:you now have to pay Rs.72 for a litre of petrol 2012 Rs 53.32=$1
Ben Bernanke does away with cheap money policy.Rupee value drops to 65 despite preventive measures.Rahuram Rajan appointed as RBI governor replacing D.Subbarao. |

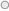


 1992 Rs 25.92=$1
1992 Rs 25.92=$1

 NOW Rs 65
NOW Rs 65